Cryptocurrencies remain a hot topic, provoking split opinions about their regulation and use. While some countries debate whether to ban crypto entirely or just particularly, others wonder how to regulate it in comparison with all common financial institutions to ensure the maximum safety for both businesses and customers. That’s where the KYC and AML laws come in, designed specifically to provide clarity and security for all participants of the constantly changing crypto ecosystem.
From registering an account on an exchange platform and launching your online crypto business to complying with the current European regulatory standards, the KYC and AML laws remain a centerpiece in terms of data protection. While these policies are closely interconnected and similar in their main objectives, compliance with them is mandatory for all crypto companies, from startups to more advanced. In this article, you’ll get a clear grasp of the practical importance of KYC and AML protocols, their practical requirements, and how they impact the operations, compliance, and long-term success of your business.
What is KYC in Crypto?
As cryptocurrency continues to change and improve, so do the regulations that govern this industry. Asking the question “What is KYC in crypto?” is crucial for any company that serves a wide range of clients and deals with sensitive financial transactions. The abbreviation stands for Know Your Customer (KYC) and refers to a set of procedures designed to verify the identity of users before using cryptocurrency services. This procedure typically includes collecting personal information such as government-issued IDs, proof of address, and, in certain cases, the user’s biometric data, like a selfie or video verification. For instance, the major exchanges like Coinbase or Binance require full KYC checks before enabling higher transaction limits or fiat withdrawals for users.
Besides the obvious safety purposes of KYC, this verification protocol helps exchanges and other types of crypto businesses obtain a crypto license in major jurisdictions and provide their services internationally. Indeed, KYC’s meaning in crypto stretches far beyond just one of the regulatory obligations. Instead, implementing strong KYC measures for your business helps create more transparent and safer conditions both for you and your clients.
KYC Requirements on Crypto-Related Transactions and Services

By verifying the identities of your clients according to the KYC protocols, you both prevent fraud and contribute to customers’ long-term trust in your company. As you move forward with registering your company and keeping it compliant in the years to come, it’s essential to know the key KYC requirements for cryptocurrency.
1. Personal data verification
This step helps your company confirm that the client’s reported location matches their identity, which reduces the risk of fraudulent accounts and shows the business’s compliance with the relevant jurisdictional regulations. First of all, passports and driver’s licenses can be used for verification as government-issued IDs. For instance, exchanges like Coinbase require customers to undergo the KYC check before they are allowed to trade or withdraw funds. It is often completed using automated ID verification tools to simplify the procedure. Additionally, high-risk customers, such as those from sanctioned countries or politically exposed persons (PEPs), undergo enhanced due diligence with additional verification.
Besides, proof of address is often required as part of the KYC policy. For that, clients have to provide documents that demonstrate their name and residential address, dated within the past three months. Customers can submit their recent utility bills, bank statements, or official government correspondence for that.

2. Customer risk assessment
Another key element of KYC protocols is evaluating the customer risks based on factors such as their transaction history and location. Proceeding with consistent monitoring of transactions helps platforms detect any suspicious activities and comply with regulations set by organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the United States, European Banking Authority (EBA) in the European Union, and others. Once a questionable activity is detected, the company is required to report it to the relevant authorities.
What is AML in Crypto?
Besides KYC protocols, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies present another centerpiece of today’s crypto regulation. If you wonder, what is AML crypto, here is what you need to know about this regulatory framework. AML laws are designed to prevent the occurrence of such illicit activities as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing. These are common challenges for digital assets today and require businesses to take effective actions to protect the integrity of their internal financial environment as well as the broader market. As a comprehensive regulatory response to these present-day demands, AML laws have become globally coordinated and increasingly stringent. They are an essential part of ensuring your company’s compliance with the current regulatory requirements in the major jurisdictions and securing its right crypto license.
Crypto AML Regulations
The AML policies in the crypto industry are designed to prevent the misuse of digital assets and illicit activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. How does it work in practice? First of all, AML requires all crypto businesses – including wallets, exchanges, and payment processors – to implement strict controls and monitoring systems. Ensuring crypto AML compliance is a significant step for your company as it enhances the security of handling transactions and your clients’ personal information.
Second, keep in mind that there are two levels of AML laws: international (or national) and in-company. The former generally refers to such regulators as the EU directives and the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) framework that was implemented in June 2023. Those navigate the crypto companies and apply the AML standards within the European Union. The in-company aspect of AML protocols, in contrast, is related to the internal policies developed within each business separately. While they still must comply with the general requirements, they provide a certain degree of flexibility in establishing the security rules best aligned with a particular company’s goals and objectives.
Here is an overview of the major practices in AML crypto regulation you can implement in your business:
Customer due diligence (CDD)
It is the foundational step in AML compliance, where crypto companies verify their customers’ identity before interacting with them and handling their sensitive financial data. Similarly to KYC, the AML procedure involves collecting the clients’ personal information, such as government-issued IDs, proof of address, and sometimes the source of funds. The goal of such regulation is to assess the risk level of each user by evaluating factors associated with their transaction records, geographic location, and the type of their activities. For instance, for higher-risk customers, enhanced due diligence (EDD) is required to gather additional information and perform deeper background checks.
Besides, AML policies are significant not only for clients but also for business operators who seek to provide their services lawfully and in full compliance with the local AML obligations. In particular, when opening a business bank account, banks often require companies to provide proof of their strong AML controls, including effective CDD procedures, to prevent risks before providing any banking services to crypto businesses.
Transaction monitoring
AML regulations require ongoing monitoring of all clients’ transactions to spot and report any unusual or suspicious behavior. Crypto platforms use advanced software and blockchain analytics tools for tracking the users’ large or rapid transfers, transactions related to high-risk countries, or activities that are inconsistent with a client’s profile. As a result, this proactive monitoring allows for detecting potential money laundering, fraud attempts, or terrorist financing in real time, which enables the company to respond promptly and take the necessary action to stop the harmful activities.
Reporting suspicious activity
Once suspicious transactions or behaviors on the clients’ behalf are identified, crypto businesses are obligated to file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) or Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) with the relevant financial authorities. These reports contain detailed information about the user completing the transaction in question. When the report is submitted, regulators and law enforcement proceed with investigating the issue and preventing similar financial crimes in the future. Otherwise, failure to report suspicious financial activities results in significant penalties and regulatory action against the company.
Consequences of Non-Compliance

While adhering to the KYC and AML policies provides numerous benefits both for your venture and clients, you might wonder what happens in case of non-compliance. What you can be certain about is that failure to implement KYC and AML regulations leads to severe consequences for any cryptocurrency business. Since regulatory authorities worldwide are increasingly vigilant, failure to meet the KYC and AML legal standards may result in hefty financial penalties, suspension, and even loss of the license. In the most severe situations, it also potentially leads to criminal prosecution of company executives.
In turn, for the client, the lack of compliance leads to their account freezing or termination, loss of access to their assets and services, such as account opening and trading, inclusion in suspicious activity reports (SARs) and blacklisting by financial institutions, and even criminal liability in the most serious cases. For instance, legal and criminal consequences apply when a service user is suspected of fraud or money laundering.
Aware of the significance of AML and KYC laws and the consequences for the businesses and clients not complying with those, at Fintech Harbor Consulting, we’ll help you understand these risks and develop robust compliance programs to safeguard your business’s long-term growth with no risks or penalties.
Best Practices for KYC and AML in Crypto
Now that you know about the nuances of the KYC and AML procedures, it’s time to take practical action and develop effective customer protection and verification policies at your company. In April of 2023, the EU Global Facility on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism provided its strategy on cryptocurrency regulation. Accordingly, the key practical steps towards ensuring safety in crypto include implementing supervision, risk assessment, and investigations.
Smart KYC and AML strategies for crypto businesses
A well-structured regulatory framework with an emphasis on KYC and AML procedures does much more than just reduce risks. Rather, it fosters secure and transparent conditions for growth and innovation in the market. You might wonder, how to proceed with effective supervision and risk assessment in practice? Here is the list of steps that will help protect your business, clients, and the broader financial system you’re part of:
- Identity verification: Full legal name, date of birth, and nationality information from a government-issued ID (can be a passport, driver’s license, or national ID card);
- Address verification: Proof of address such as a utility bill, bank statement, or lease agreement (dated within the last 3-6 months);
- Photographic evidence: Selfie holding ID or a specific handwritten note for additional authentication;
- Phone number and email verification: Valid mobile number and email address for contact and security purposes;
- Source of funds: Declaration of the funds’ origin used for crypto transactions (e.g., salary, inheritance, investments);
- Risk assessment and monitoring: Ongoing monitoring of transactions for suspicious activity and risk rating of customers based on behavior and geography;
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Additional checks for high-risk individuals or large transactions; may also include financial documents, employment details, or income statements;
- Sanctions and PEP (Politically Exposed Person) screening: Check customers against international sanctions lists and identify individuals with high public influence or political exposure;
- Compliance with jurisdictional regulations: Adherence to local and international AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws and registration with financial authorities, if applicable;
- Record keeping: Maintain records of all customer data and transactions for at least 5 years (varies by jurisdiction).
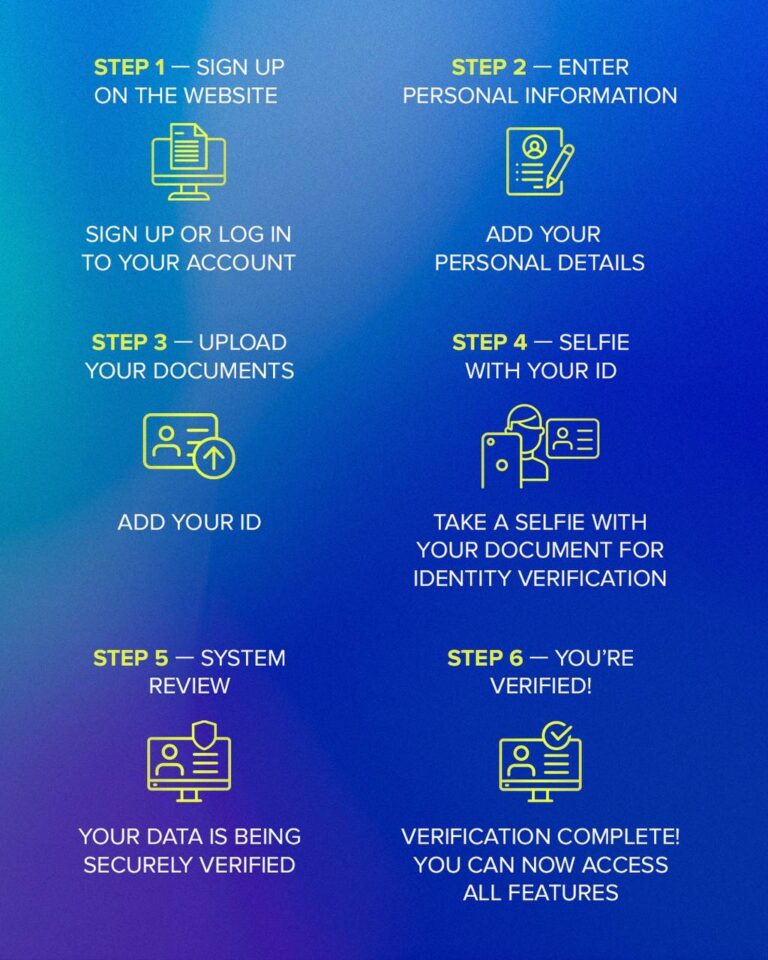
Client’s guidelines for passing identity verification
If you’re about to proceed with your personal verification on the online platform, it’s important to know how to simplify this process and pass it successfully on the first attempt. Here is your roadmap for each verification step:
Conclusion
In the fast-moving world of crypto, regulatory challenges and solutions to them are evolving rapidly. Navigating such a financial landscape, with its growing demands, takes more than matching generic checklists. Rather, it calls for a strong, future-oriented strategy for weaving the KYC and AML standards into the core of your business. At Fintech Harbor Consulting LTD, we fully acknowledge the vital role of KYC and AML laws and offer end-to-end support in handling the complex regulatory web across various jurisdictions. Therefore, we provide end-to-end support in drafting the customized AML protocols for your company in full compliance with the regulatory requirements, specifically in your selected jurisdiction.
We’ll make sure your venture meets the highest security standards from day one and ensure your company’s full compliance in the long run. Efficient regulation and implementation of KYC and AML protocols bring a range of benefits for your business as well as other market participants, including:
- Market confidence: Smart regulations provide a harmonized legal structure for using crypto;
- Consumer protection: Helps to prevent fraud and ensure adherence to legal standards by wallet and exchange providers;
- AML/KYC compliance: Prevents money laundering and terrorist financing;
- Taxation: Allows governments to collect taxes on cryptocurrency transactions, which can be difficult to track without proper regulation;
- Implementation of enforcement legislation: Allows regulators to carry out professional, independent investigations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key KYC requirements for cryptocurrency businesses?
The major KYC requirements for cryptocurrency businesses involve verifying the identity of clients before allowing them to access the services. This process typically includes the following practical steps toward confirming that your clients are exactly who they claim to be:
- Collecting government-issued identification;
- Proof of the customer’s address;
- Collecting the client’s biometric data (in certain cases);
- Proceeding with ongoing transaction monitoring;
- Conducting customer risk assessment.
How do AML and KYC regulations apply to crypto exchanges and platforms?
AML and KYC laws apply directly to crypto exchanges and platforms, requiring them to monitor users’ activities and detect any suspicious behavior. This means that crypto platforms must develop robust compliance systems to verify user identities, assess high-risk profiles, and immediately flag potentially illicit behavior. Jurisdictions like Singapore, the European Union, and the United States have already enacted strict AML and KYC requirements. AML policies, for instance, are related to the crypto companies much closer than you might think. While some might associate those laws with banks and financial institutions only, they actually require all crypto exchanges to comply with AML, according to the 5th and 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLDs).
If you ever questioned the security of KYC laws, be certain that the major platforms encrypt and store their data – including the personal or sensitive information – in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) standards, which refer to the EU regulation that has been in force since 2018. As the blockchain technology continues to evolve and expand rapidly, GDPR aims to help users regain full control over their data and make businesses that handle that information responsible for protecting their clients’ privacy. Circling back to the KYC protocols, they are part of this structure designed to protect both the companies and customers while providing them with control over their data and holding them accountable for their crypto activities.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with KYC and AML regulations in crypto?
While there is no doubt that KYC and AML laws are essential for lawful and transparent business operations, this is what you should know about what happens if a company fails to comply with those policies. First of all, non-compliance with KYC and AML can lead to heavy fines and suspension or revocation of crypto licenses. Moreover, in the most critical situations, businesses may be subject to criminal liability for company executives.
In addition to legal risks, the reputational damage caused by non-compliance with protocols can be just as severe. Loss of trust from customers, investors, and business partners would significantly hinder the company’s growth and its market access. Major exchanges and crypto corporations have faced multi-million-dollar penalties as well as operational bans for one reason: failure to implement proper KYC and AML protocols. For instance, the OKX cryptocurrency exchange was already penalized for $504 million for violating the US AML laws in 2025, Robinhood Financial LLC – $29.75 million, and Admiral Casino – £1 million.
Overall, as regulators worldwide increase their oversight over cryptocurrency activities, businesses are expected to follow strict compliance guidelines from day one. Non-compliance with KYC and AML laws not only exposes a business to serious legal penalties but also increases the risk of being misused for money laundering, fraud, or terrorist financing activities.











