- 9 minutes read
Table of contents
In simple words – a company credit score is a measurement of the risk of a financial institution lending credit to a business. Although, the company credit rating is used not only when approving lending programs, but can also serve as a reason for refusing to work with a client at all. In today’s world, a good business credit rating can avoid a lot of problems for a business.
In this article, we will discuss how you can increase your company credit score, what factors affect it, how it is calculated, and give some examples of organizations that provide credit scores to businesses.
Quickly select a jurisdiction and register your company anywhere in the world online

What is a business credit rating?
A business credit rating is an indicator that shows whether a financial institution can trust your company with its money. Banks, insurance companies and other financial organizations that work with private clients usually have a credit rating. By the company credit rating you can understand how stable it is: if it is high, it means that the business is doing well, the company pays its bills and it is safe to give loans and make deals. If the business credit score is low, the business faces restrictions such as less flexible payment terms with suppliers, smaller loan amounts and many others.
You can run a company credit score check online within a few minutes. You will just need to go to the website of one of the credit bureaus, register and apply.
The credit rating of a company affects its activities quite a lot. In case it is high enough, the company gets a lot of new opportunities. The business can be profitably insured, get a loan under good terms, and have flexible payment terms with suppliers. With a good credit rating, your company will almost never be turned down for renting premises, opening an account or partnership.
However, if you allow late payment of invoices, loss of reputation or risk of bankruptcy, the company’s credit rating may become low. This threatens to tighten credit, insurance and supply terms, as well as limiting your ability to finance the company and acquire new partnerships.
Have questions? Contact us!
*Your contact information will be used for our inner purposes and only with the aim to provide you with the best business solutions.
Meaning of the company credit score?
In general, there is not much difference between credit rating and company credit score. The credit rating is denoted by letters, for example – AAA, AA, A, BBB, BB, B, CCC, CC, C, C, and D. Using this method, the highest rating is AAA, while at the same time D is the default. But, this method is used mainly when calculating credit ratings for states or its governments or huge corporations. So it is not very suitable for small and medium-sized businesses.
Unlike the previous indicator, the company credit score uses numbers. Usually, for simplicity, values from 0 to 100 are used, where 100 is the highest rating. But you can also find other scales. For example, from 300 to 850 (This scale is more typical of the American system).
In addition, some organizations may also use a more non-standard scale. For example, “negative,” “positive,” “stable. But it is rarely used.
How is a company’s credit score calculated?
The company’s credit rating is calculated in several ways, as the algorithms of different rating agencies differ.
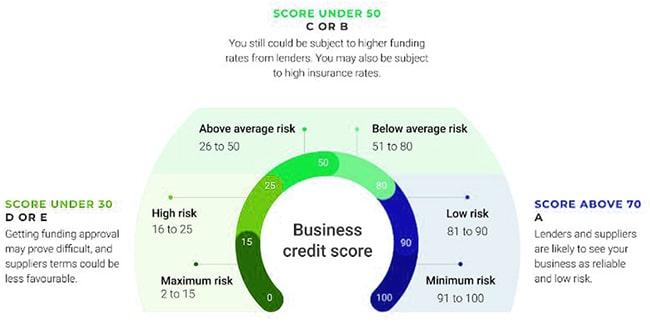
Company credit scores for companies usually range from 0 to 100, indicating the following levels of risk:
- Low risk – a score between 80 and 100
- Medium risk – a score between 50 and 79
- High risk – a score between 0 and 49
FICO Agency (USA) scores range from 300 to 850.
- A poor score is between 300 and 579,
- Fair score is from 580 to 669,
- Good score is from 670 to 739,
- Very good score is from 740 to 799
- And an exceptional score is from 800 to 850.
The credit rating is calculated based on many factors, such as return on equity and assets, completeness and clarity of the company’s financial information and reports, the amount of debts and the speed of their repayment, and more.
Factors affecting your company’s credit rating
Therefore, there are a lot of factors influencing the credit rating of a company. Currently, financial institutions (including banks) calculate the rating using automated tools that collect data about the company on the Internet, as well as process the provided documents. In this regard, thousands of different factors can affect the rating. But, at the same time, not all factors are decisive. We will give a few really important ones as an example.
- The size of the company and the length of time it has been in business.
- The industry in which your business operates (some industries are riskier than others).
- Length of credit history (The longer a company’s credit history, the better).
- Payment history. Shows how much the company has previously borrowed and whether it has paid on time.
debt usage - Number and frequency of previous applications for finance – whether they have been approved or rejected.
- The company’s accounting records and tax returns
- Details of the company’s directors, shareholders and other business partners
- Outstanding County Court Judgments (CCJs)
- Any signs of business insolvencies
How to improve your business credit score?
1. Complete review of all payment history data that is posted on public credit rating bureaus
You should check the information about you that can also be seen by your partners, suppliers and any other interested parties. If there are any inaccuracies that negatively affect your credit rating, you should correct them as soon as possible by sending a request to the credit rating bureau.
Important: You must have proof of the financial transactions you want to correct.
2. Do not leave the сredit balance at zero
If your credit history is empty, it does not promise you a good rating. Try to take out small loans and pay them back on time. This will positively affect both the amount of future loans and your credit rating. If no opened credit account is used at all, the company will not receive the maximum credit rating. On the contrary, it will negatively affect the company’s rating worse over time.
3. Maintain a low utilization rate of available credit
This means that you should use no more than 25% of your available credit. For example, with a 100,000 pound credit limit, only use 25,000 pounds of it. Try to bring your account balance to zero as often as possible. This will prove that you are solvent and at the same time increase the confidence of lenders as well as your suppliers and partners.
If you are not within this ratio, try increasing your company’s credit limit. This way, your spending will remain the same and your credit utilization ratio will decrease.
4. Control over counterparties
Your credit rating often depends not only on you, but also on the people you work with. Make sure that your counterparties enter the correct information about your overall transactions into your financial report to the credit bureaus on time.
5. Avoid the courts
A company’s credit rating can go down because of the initiation of litigation. And you can be either a plaintiff or a defendant – often this does not affect, as the credit bureaus are mostly focused on the amount of legal expenses you have incurred or will incur in the future. Try to settle things amicably and negotiate without going to court.
6. File annual accounts and tax returns on time and keep your business details up-to-date
Many jurisdictions already have automated business databases that are open to all. In case of changes, enter them there too, so that the profile looks alive. Also avoid problems and fines from local regulators.
7. Ensure the cyber security of your company
Protecting data and information is now an important issue not only for businesses, but also for credit bureaus. Cybersecurity weaknesses can lead to customer data leakage, which in turn leads to financial and legal problems. Try to ensure your company has sufficient data protection and minimize the risks of information leakage. This is especially important for FinTech scope.
FAQ
Why it is important to regularly check a Company Credit Score
In case of unsatisfactory values, you will have an understanding that you need to take some action. In case of a good rating, you will be able to show additional evidence to financial institutions and counterparties of the stability of your business.
How will a bad credit rating affect my business?
A low credit rating directly affects a company’s operations. A business in this situation faces increased business expenses, limited flexibility in payment terms with suppliers, higher insurance premiums, weakened creditworthiness, lease rejections, loss of new accounts and partnerships, or other problems.
How long will it take to improve my business credit score?
Improving a credit rating is, of course, more difficult than lowering it. This process takes from a couple of weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the situation. For example, if you submit a record of timely debt payment to the credit rating agency and confirm this operation with documents, you will see a positive difference in your rating within 10 business days. However, other operations such as lowering the credit utilization ratio take much longer.
The difference between your credit rating and company credit rating
Your personal credit rating and your company credit rating are not the same thing. A company credit rating is an indicator that shows how solvent a business is, while your personal credit rating is your ability to pay. Depending on the form of your business, your credit rating may have a stronger or weaker effect on your company credit rating. For example, if you are a sole-proprietor, much less use personal accounts to run your business or take out a personal liability loan, your credit score will have a strong impact on your business credit rating. If the company is of a different organizational form, however, it is likely that your credit ratings will have little or no effect on each other, except in isolated cases.
How to check a company’s credit score in the UK?
There are several major credit agencies in the UK – Experian, Equifax, Dun & Bradstreet and others. To run a business credit score check, you need to go to the website of one of the credit bureaus, register and apply. Next, you need to generate a credit report for your company, where you will have the “My business credit score” section available to you. Some agencies also provide Business Credit Risk Score and Business Failure Score right away. Try to check a business credit score with several credit bureaus at the same time, as information may vary. Do not forget that you can always challenge your credit rating and contact the agency to correct errors.
Conclusion
A company credit score is an important metric that should not be ignored. Importantly, the indicator is directly based on the company’s credit history, so it will not be possible to change it quickly in 90% of cases. So pay attention to it now to avoid problems with financial institutions and with counterparties in the future.













